Genetic DNA tests for inherited disorders
of cavalier King
Charles spaniels
Cavalier King Charles spaniels may have mutations in their DNA which are associated with a variety of debilitating inherited disorders. They include:
Chondrodystrophy (CDDY) – causing degeneration of discs between the vertebrae.
Curly Coat Syndrome – severe congenital condition of the skin, coat, claws, and eyes.
Degenerative Myelopathy (DM) – a crippling neurological disease of the spinal cord.
Episodic Falling Syndrome (EPS) – involuntary contraction of muscles.
Medium chain triglyceride (MCT) mutation (MCADD) – causing recurrent, prolonged seizures.
Muscular Dystrophy (MD) – progressive lack of stability of the sketetal muscles.
Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA) – blindness due to degeneration of the retina.
Xanthinuria – crystals or sediment in the urinary tract.
For details about the specific mutations associated with each of these disorders, click on the highlighted names above, which are linked to the DNA section of each of the webpages discussing the disorders.
RETURN TO TOP
Gene Mutations Diagnose Disorders
These genetic mutations may be detected by obtaining samples of the cavalier’s DNA by swabbing its mouth with a cotton swab or by drawing blood. Once a genetic mutation is confirmed, that information may be used to accurately diagnose the dog’s disorder and enable it to be properly treated.
RETURN TO TOP
Genetic Testing Laboratories
 Several genetic testing laboratories throughout the world offer
specific DNA tests of the cavaliers’ saliva and/or blood samples to detect
whether the dogs have any of the mutations causing these disorders.
However, not all labs test for all disorders. The current list of
genetic testing labs, and the disorders they test, are, alphabetically:
Several genetic testing laboratories throughout the world offer
specific DNA tests of the cavaliers’ saliva and/or blood samples to detect
whether the dogs have any of the mutations causing these disorders.
However, not all labs test for all disorders. The current list of
genetic testing labs, and the disorders they test, are, alphabetically:
• American Kennel Club (AKC) -- Curly Coat Syndrome, Degenerative Myelopathy, Episodic Falling Syndrome
• Antagene – Curly Coat Syndrome, Degenerative Myelopathy, Episodic Falling Syndrome, Muscular Dystrophy, Skeletal Dysplasia 2, Xanthinuria
• Canine Genetic Diseases Network, University of Missouri – Degenerative Myelopathy, Progressive Retinal Atrophy
• Canine Genetics Lab, University of Minnesota College of Veterinary Medicine – Xanthinuria
• Canine Genetic Testing (CAGT), University of Cambridge Dept. of Veterinary Medicine – Curly Coat Sydrome, Degenerative Myelopathy, Episodic Falling Syndrome, MCAD Deficiency, Progressive Retinal Atrophy
 •
DDC DNA Diagnostics Center – Degenerative Myelopathy,
Progressive Retinal Atrophy
•
DDC DNA Diagnostics Center – Degenerative Myelopathy,
Progressive Retinal Atrophy
• Embark, Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine – Chondrodystrophy, Curly Coat Syndrome, Degenerative Myelopathy, Episodic Falling Syndrome, Muscular Dystrophy, Progressive Retinal Atrophy, Xanthinuria
• GenSol Animal Diagnostics – Chondrodystrophy, Curly Coat Syndrome, Degenerative Myelopathy, Episodic Falling Syndrome, MCAD Deficiency.
• Laboklin – Chondrodystrophy, Curly Coat Syndrome, Degenerative Myelopathy, Episodic Falling Syndrome, MCAD Deficiency, Muscular Dystrophy, Progressive Retinal Atrophy, Xanthinuria
• MyDogDNA, Wisdom Panel – Chondrodystrophy, Degenerative Myelopathy, Episodic falling syndrome, Muscular Dystrophy, Xanthinuria
• Orivet – Chondrodystrophy, Curly Coat Syndrome, Degenerative Myelopathy, Episodic Falling Syndrome
• Paw Print Genetics – Chondrodystrophy, Curly Coat Symdrome, Degenerative Myelopathy, Episodic Falling Syndrome, Progressive Retinal Atrophy
• Veterinary Genetics Laboratory, University of California - Davis Veterinary Medicine – Chondrodystrophy, Degenerative Myelopathy, Progressive Retinal Atrophy
RETURN TO TOP
How Is The Sample Obtained?
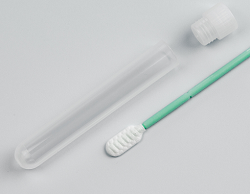 In most all cases, the DNA sample is obtained from the dog’s mouth,
using a cotton tipped swab. The laboratory will send a “test kit” with
one or more cotton swabs and a storage container and return envelope.
The owner will be directed how to insert the swab into the dog’s mouth,
against the gums, for up to a minute, to collect saliva.
In most all cases, the DNA sample is obtained from the dog’s mouth,
using a cotton tipped swab. The laboratory will send a “test kit” with
one or more cotton swabs and a storage container and return envelope.
The owner will be directed how to insert the swab into the dog’s mouth,
against the gums, for up to a minute, to collect saliva.
Watch
this YouTube video to learn how to properly use a swab to obtain DNA from
![]() your dog. If blood samples are required for the testing, a veterinarian should
obtain the blood and handle shipment to the laboratory.
your dog. If blood samples are required for the testing, a veterinarian should
obtain the blood and handle shipment to the laboratory.



CONNECT WITH US